Email has been one of the primary ways of communication all over the world especially in the Corporate World. Not only emails are used for communication a lot of confidential information is also shared via emails. Every day around 269 billion of emails is sent across the globe. These numbers are huge enough to intrigue hackers and cyber-bullies to use emails as their target for cybercrime.
Over the years a number of email scams have been identified Email Spoofing being one of them. But what is Email Spoofing? And how can you mitigate it? In this blog, we will address these two questions. In the end, we will tell you how Diadem can help you mitigate email spoofing with some great tools.
What is Email Spoofing?

Spoofing generally means to hoax or trick someone. And that’s what Email Spoofing is all about. Hackers during a spoofing attack masquerade themselves as someone else by falsifying data. This helps them in gaining an illegitimate advantage over the person’s confidential data.
Types of spoofing Attacks:
There are various types of Spoofing Attacks. Few of them are:
- TCP/IP address spoofing
- Referrer Spoofing
- Poisoning of file-sharing networks
- Caller ID spoofing
- email spoofing
- GPS spoofing
- DNS spoofing
Here, we would incline your discussion more on Email Spoofing. This is because Email Spoofing has been a major concern in the Corporate World. This is mainly because in the corporate world all the communication and information sharing takes place through emails. So even if the hackers are able to spoof some of the primary emails of a company they can cause some serious losses to the business.
E-mail Address Spoofing
Email spoofing is basically executed by sending email messages with misleading sender address so as to mislead the recipient asking them to act according to the emails sent.
Commonly, the spoofed emails are sent modifying the sender name or email address. Also, sometimes the body of the message is formatted in such a way that it appears to be legitimate to the recipient.
Ways of E-mail Spoofing
There are multiple ways of Email Spoofing some of them are discussed below:
-
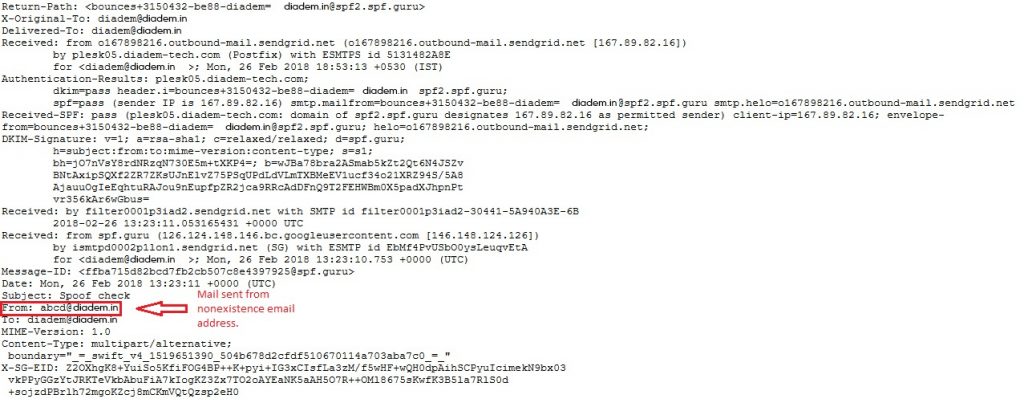
- FROM name/ address: This address is generally present in the header of the email and is visible to the end user. This particular name is spoofed.
- REPLY-TO name/ address: This address specifies the mail where on reply the mail will be delivered. This is in general, kept hidden so the details are not visible to the end user.
- RETURN-PATH address: Generally present in the header and are not visible to the user.
- SOURCE IP address or “X-ORIGIN” address: This contains the source IP address from where the mail has been sent. The sender’s origin IP can be modified to or replaced with other IP address.
The hackers very trickily send those types of mail which basically ask for renewing of the email addresses. They may also hack the email address asking the recipient to change their password from the given link. Emails from your CEO/MD or account department asking the recipient to update the new account details is one of the common examples of Email Spoofing. This type of attack especially happens when the specific email address password gets hacked and the hacker tracks specific emails and patterns. They spoof the return path so when replied it receives to the spammers. There is no default configuration set to mitigate the spoofing attack in emails.
We at Diadem, implement securities to mitigate the Spoofing. Usually, we increase the DNS sensitivity by adding the SPF records, DKIM and DMARC policy.
SPF: Sender Policy Framework(SPF) is a method of fighting spam emails where we define the set of hosts which designates outbound mailer for the domain. In the DNS zone, we need to add the record in the TXT record. You can configure SPF from this link: http://www.openspf.org/SPF_Record_Syntax
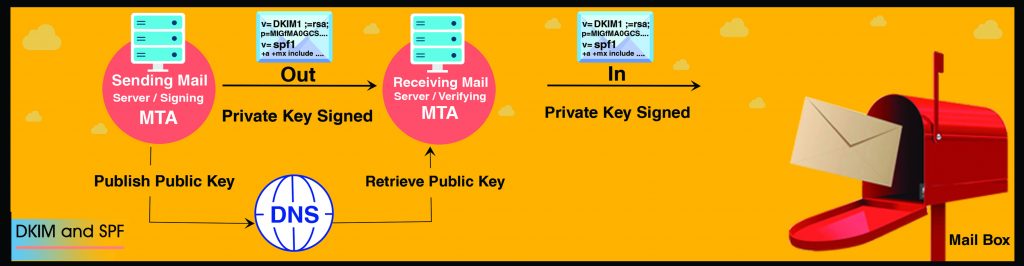
DKIM: Domain Keys Identified Mail(DKIM) is also a security measure that is taken by adding DNS record. This is done by adding a signature in the email message which is generated by the MTA(Mail Transport Agent).
In DKIM there is a public key and a unique string is generated against that particular domain which is stored in the server. After the mail is received the recipient MTA verify the signature by recovering the signer’s public key through DNS. It then uses that key to decrypt the hash value in the email’s header and simultaneously recalculate the hash value for the mail message it has received. If these two matches then the email is verified and is accepted. To generate and check DKIM you can visit the Link: http://dkimcore.org/tools/
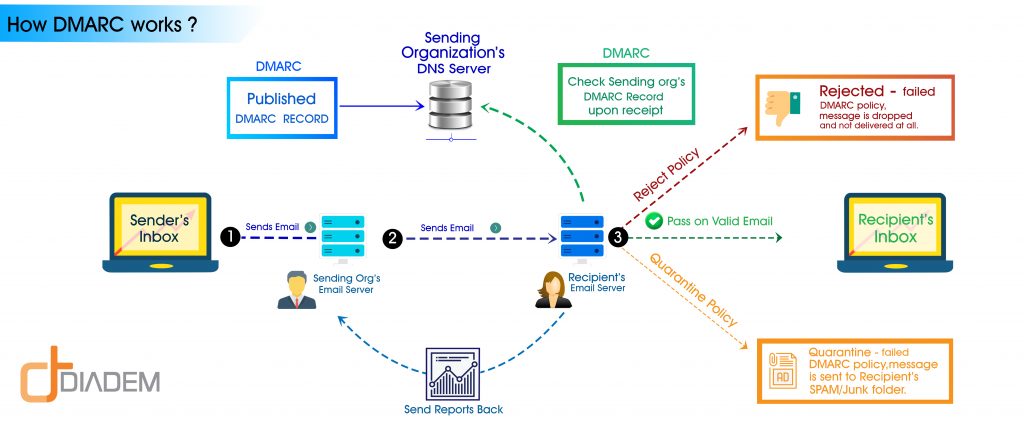
DMARC:Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance(DMARC) is an email authentication, policy, and reporting protocol. It works on SPF and DKIM protocols. This is a procedure of adding a TXT value in the DNS zone.
DMARC policy states that the sender has SPF and/or DKIM protection on that domain and also defines what action or measure needs to be taken if the SPF and/or DKIM fails. DMARC policy reports back to the domain owner about the failure.
At Diadem:
We at Diadem, provide all these securities to our customers. We provide hosting to our client where we enable checking of DKIM and DMARC for internal emails. Also, we have a premium anti-spam filter where SPF, DKIM and DMARC are checked which stops the spoof emails. This stops the spam emails to reach the user’s mailbox. This saves our clients time without the need of identifying valid emails and concentrate on their business for their business growth. To know more about our Spam Filter explore the following link: https://diadem.in/premium-email-antispam/
Also, for further assistance on the process of enabling the security in Plesk and Zimbra mail server you can check out our KB section.
Shield Your Business from Email Threats
Contact us to get our Premium Anti-Spam Filter Today